548Uploads
208k+Views
81k+Downloads
All resources

OCR A Level Physics: Newton's Law of Gravitation
OCR A Level Physics:Newton’s Law of Gravitation presentation, homework and answers.

GCSE Physics: Gravitational and Elastic Energy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.1.7 Gravitational and Elastic Energy
Energy transfers with links to sport and PE.
Employer-mentor links with physics and sports
Exam Style Question with worked solutions
Rearranging equations
Practice Questions with worked solutions

GCSE Physics: Work Done, Kinetic and Thermal Energy
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.1.3 Work Done, Kinetic and Thermal Energy
Comes complete with students activities and fully worked solutions.
Energy transfers to thermal store.
Thermal energy, equation, and specific heat capacity.
Work done equation and kinetic energy equation.
Rearranging equations.
Applying equations.
Student questions with fully worked solutions.

GCSE Physics: Electrical Power and Work Done
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P7.2.1 Electrical Power and Work Done. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Definition of power
Converting between W and kW
Converting between seconds, minutes, and hours
Calculating work done in kWh and J
Converting between kWh and J

GCSE Physics: Forces in Collisions
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P8.1.4 Forces in Collisions. All presentations come with student activities and worked solutions.
Large accelerations produce large forces.
Values of g that cause severe injury or death
Road Safety
Newton’s First Law and seat belts
Crumple zones
Force = Mass x Acceleration
Acceleration = Change in velocity /Time taken
Estimating speed, accelerations and forces involved in large accelerations for everyday road transport.

OCR A level Physics: Uses of capacitors
OCR A level Physics: 21.5 Charging Capacitors
Module 6 Particles and Medical Physics
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Calculating power output from a circuit containing a capacitor
A rectifier circuit - changing an alternating input to a smooth output

GCSE Biology: Animal and Plant Cells
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.1.1 Animal and Plant Cells
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Cells are the building blocks of living objects.
Definition of eukaryotic cells
Typical size of eukaryotic cells
Subcellular structure of animal cells
Subcellular structure of plant cells
Organelles and their functions
Revision activities (Look, Cover, Write, Check)
Print out of animal and plant cells

GCSE Biology: Bacterial Cells
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.1.2 Bacterial Cells
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Typical size of bacterial cells
Subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Functions of subcellular structure of bacterial cells
Comparing animal, plant, and bacterial cells
Revision activity - flash cards
Print out of bacterial cell

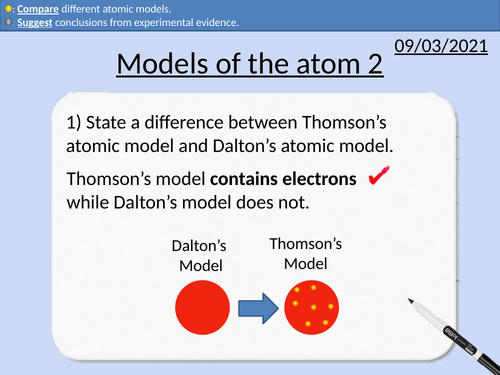
GCSE Physics: Development of the Atomic Model 2
This presentation includes:
Why scientific models change over time
Electric charge
Rutherford’s atomic model
Rutherford’s experiment
Bohr’s atomic model
Bundle

GCSE OCR Biology: B1 Matter Full Scheme
All resources for B1 GCSE OCR Biology Gateway 9-1.Triple and combined (Higher and Foundation) is covered in this material.
Includes:
Plant and animal cells
Bacterial cells
Light microscopes
Electron microscopy
DNA
Transcription and translation
Enzymes
Enzyme reactions
Carbohydrates, proteins, and lipids
Aerobic respiration
Anaerobic respiration
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis experiments
Factors affecting photosynthesis
Interaction of limiting factors

GCSE Biology: Osmosis
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B2.1.2 Osmosis
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Definition of osmosis.
Explaining water potential and concentration of solution.
How cells change during osmosis - turgid, lysis, crenated, plasmolysed

OCR A Level Physics: Gravitational Fields
OCR A Level Physics: Gravitational Fields presentation, homework and answers.

GCSE Biology: Exchange and Transport
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B2.2.1 Exchange and Transport
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Calculating total surface area of a cube
Calculating volume of a cube
Calculating surface area to volume ratio
Exchange surfaces in the alveoli and villi
A large surface area to volume ratio allows diffusion to occur.

GCSE Biology: Circulatory System
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B2.2.2 Circulatory System
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
The circulatory system is a closed system.
Recap: Aerobic Respiration
Structure of arteries, veins, and capillaries.
Blood flows through the heart twice in every circuit of the body - the double circulatory system.

GCSE Biology: Heart and Blood
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B2.2.3 Heart and Blood
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Left and right in the heart
The four chambers of the heart
Labeling the heart
Circulation of blood around the body
The components of blood and their functions
Plasma
Red blood cells
White blood cells
Platelets

GCSE Biology: Factors Affecting Transpiration
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B2.2.6 Factors Affecting Transpiration
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Factors that affect the rate of transpiration:
Light intensity
Temperature
Air movement (wind)
Humidity.
How open stomata increase the rate of transpiration.
Graphs of rate of transpiration against different variables.
Concentration gradients and rate of transpiration
Calculations of the rate of transpiration.

GCSE Biology: Transpiration Stream
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B2.2.5 Transpiration Stream.
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Water diffuses into the root hair cells by osmosis.
Water moves up the stem through the xylem.
Water is lost from leaves by evaporation through open stomata.
Labelling the stomata
The role of the cuticle
How water loss efftects the stomata

OCR AAQ in Applied Science: P1.1.4 Series and parallel circuits
Course: OCR Level 3 Alternative Academic Qualification Cambridge Advanced Nationals in Applied Science.
Topic Area P1: Electricity - 1.1.4 Series and parallel circuits
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Circuit symbols
The relationships between currents, voltages and resistances in series and parallel, including how potential difference varies for cells in series.
Know Conservation of charge and Kirchoff’s first law
Know Conservation of energy and Kirchoff’s second law
Solving for resistors in series
Solving for resistors in parallel

OCR AAQ in Applied Science: P1.1.2 Potential difference and resistance
Course: OCR Level 3 Alternative Academic Qualification Cambridge Advanced Nationals in Applied Science.
Topic Area P1: Electricity - 1.1.2 Potential difference and resistance
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Know the definition of potential difference, with respect to work done
Know the unit of potential difference
How resistance is defined by: Resistance (Ω) = potential difference (V)
current (A)
Know the unit of resistance
I-V characteristics of resistor, light-dependent resistor (LDR), filament lamp,
thermistor, diode and light-emitting diode (LED)
Use of the equation: Potential difference (V) = current (A) × resistance (Ω)
Know Ohm’s law
Resistance of NTC thermistors with temperature, and resistance of LDRs with light intensity

OCR AAQ in Applied Science: P1.1.1. Charge and current
Course: OCR Level 3 Alternative Academic Qualification Cambridge Advanced Nationals in Applied Science.
Topic Area P1: Electricity - 1.1.1. Charge and current
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Know the definition of electric current in metals and electrolytes
Know the unit of current
Conventional current and electron flow
Direct current
Know the unit of charge
Elementary charge, e, including charge of an electron and proton
Use of the equation: Charge © = current (A) × time (s)