Resources included (10)
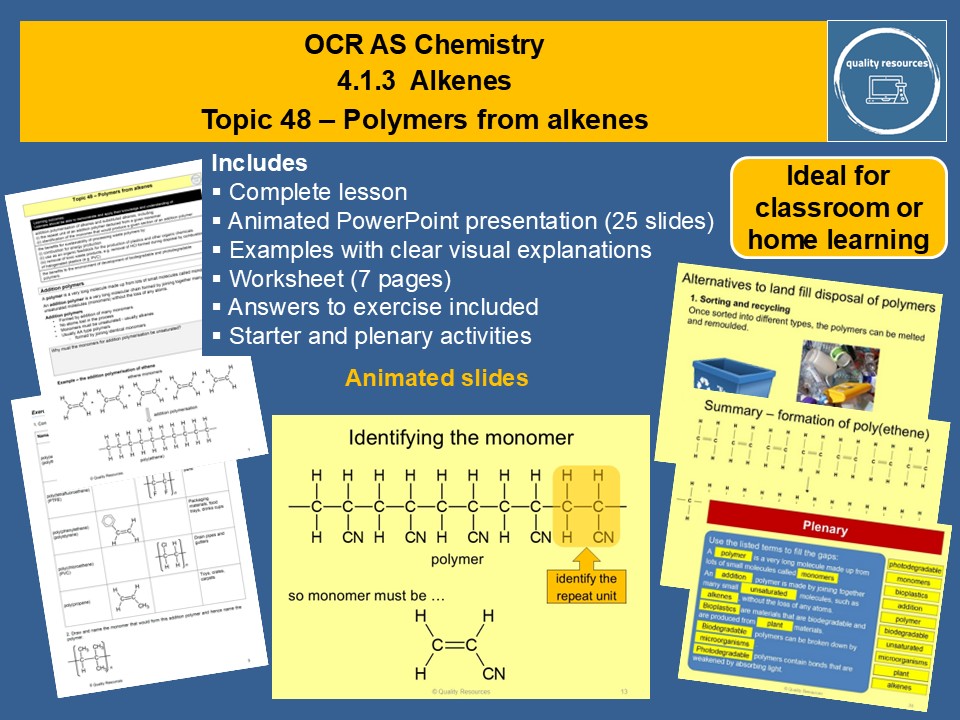
Polymers from alkenes OCR AS Chemistry

Alkenes OCR AS Chemistry

Reactions of alkanes OCR AS Chemistry

Introduction to alkanes OCR AS Chemistry

Organic reagents and types of reaction OCR AS Chemistry

Isomerism OCR AS Chemistry

Functional groups - names and formulae OCR AS Chemistry

Quiz - A question of naming alkanes

Naming hydrocarbons OCR AS Chemistry

Introduction to organic chemistry OCR AS Chemistry
This bundle covers all of the OCR A level chemistry specification section 4.1 (basic concepts of organic chemistry and hydrocarbons).
The resources included are:
- Introduction to organic chemistry
- Naming hydrocarbons
- Quiz – A Question of naming alkanes
- Functional groups – names and formulae
- Isomerism
- Organic reagents and types of reaction
- Introduction to alkanes
- Reactions of alkanes
- Alkenes
- Polymers from alkenes
Each topic includes a fully interactive PowerPoint including starter, group activities, questions and plenary along with a worksheet. Answers to all exercises are provided. Some of the resources include a PowerPoint quiz and all are ideal for classroom or home learning.
This bundle is part of a series covering the OCR AS Chemistry specification and relates to the following sections:
Module 4– Core organic chemistry
Part 1 – Basic concepts and hydrocarbons
4.1.1 basic concepts of organic chemistry(all)
4.1.2 alkanes (all)
4.1.3 alkenes (all)
Content covered:
Introduction to organic chemistry
• Why carbon is special
• Bonding in organic compounds
• Different types of formulae
• Types of organic compounds
• Functional groups and homologous series
Naming hydrocarbons
• Application of IUPAC rules of nomenclature for systematically naming organic compounds
• Naming alkanes and cycloalkanes
• Naming branched alkanes
• Naming alkenes and branched alkenes
Quiz – A Question of naming alkanes
Functional groups – names and formulae
• Application of IUPAC rules of nomenclature for systematically naming organic compounds
• Practice naming organic compounds including those with functional groups
• Revision of empirical and molecular formula and how to calculate them
• Formulae of compounds with functional groups
Displayed formula
Structural formula
Skeletal formula
Isomerism
• Shapes of alkanes (with model building)
• Definitions of structural isomers, stereoisomers, E/Z isomers and cis-trans isomers
• Classification of isomers with examples
• Structural isomers including chain, position and functional group isomers
• Shapes of alkenes (with model building)
• Restricted rotation around the C=C double bond
• Stereoisomers – E/Z and cis-trans isomers
• Animated illustrations of E/Z isomers
• Criteria for E/Z isomerism and for cis-trans isomerism with examples and learning check
• Cahn-Ingold-Prelog rules for naming E/Z isomers with examples
Organic reagents and types of reaction
• Ways of breaking covalent bonds
Homolytic fission
Heterolytic fission
• Types of organic reagents and their reactions
Nucleophiles
Electrophiles
Radicals
• Introduction to mechanisms
• Curly arrows
• Types of reaction
Addition
Substitution
Elimination
• Classification of reactions
**Introduction to alkanes **
- Sources and uses of alkanes
- Definitions of fossil fuels and crude oil
- Uses of alkanes as fuels
- Bonding in alkanes
- Formation and rotation of sigma bonds
- Shapes of alkanes
- Intermolecular forces in alkanes in terms of non-polar molecules
- Melting and boiling points of alkanes in terms of London forces
- Effect of chain length and branching on London forces
Reactions of alkanes
- Reactivity of alkanes
- Combustion of alkanes – complete and incomplete
- Balancing combustion equations
- Radicals and dot-and-cross diagrams
- Radical chain reactions
- Radical substitution of alkanes by halogens
- Mechanism including initiation, propagation and termination
- Limitations to the use of radical substitution in synthesis of halogenoalkanes
Alkenes
- Structure and reactivity of alkenes
- The nature of the double bond – sigma and pi bonds
- Explanation of restricted rotation around C=C
- Shape of ethene in terms of electron pair repulsion theory
- Addition reactions of alkenes
- Reactions of ethene and propene including addition of halogens, steam, hydrogen halides and hydrogen
- Test for alkenes with aqueous bromine
- Catalytic addition of hydrogen - mechanism
- Margarine manufacture
- Definition of electrophile
- Electrophilic addition mechanism
- Addition of HX to unsymmetrical alkenes - Markownikoff’s rule and explanation
Polymers from alkenes
- meaning of the terms addition polymer and monomer
- the formation of poly(ethene)
- general equation for polymer formation
- identifying the monomer from the repeat unit of the monomer
- disposal of waste polymers by recycling, cracking and combustion
- bioplastics
- biodegradable polymers
- photodegradable polymers
Links
Next lesson: chemistry of alcohols
/teaching-resource/chemistry-of-alcohols-as-chemistry-12273938
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
