548Uploads
208k+Views
81k+Downloads
All resources

OCR AAQ in Applied Science: 2.2 Collecting scientific data
Course: OCR Level 3 Alternative Academic Qualification Cambridge Advanced Nationals in Applied Science.
Unit F181: Science in society
Topic Area 2: Handling scientific data
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Methods of collecting data with their advantages and disadvantages.
Observation and measurement from experiments
Surveys
Cohort studies
Meta-studies
Computer modelling
Sampling techniques
Random sampling
Systematic sampling
Using estimates
Bias and diversity in science

OCR AAQ in Applied Science: 2.1 Types of scientific data
Course: OCR Level 3 Alternative Academic Qualification Cambridge Advanced Nationals in Applied Science.
Unit F181: Science in society
Topic Area 2: Handling scientific data
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Qualitative and quantitative data
Continuous and discrete data
Primary and secondary data
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Forces in Action
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 3: Forces in Action.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from weight as a force to Archimedes’ principle.

GCSE Chemistry: Electrolysis of Water
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
• Pure water being made partially of ions (hydrogen and hydroxide).
• PANIC convention for electrodes
• OILRIG convention for redox reactions
• Electron transfers at electrodes
• Half-equations for anode and cathode
• Balancing half-equations

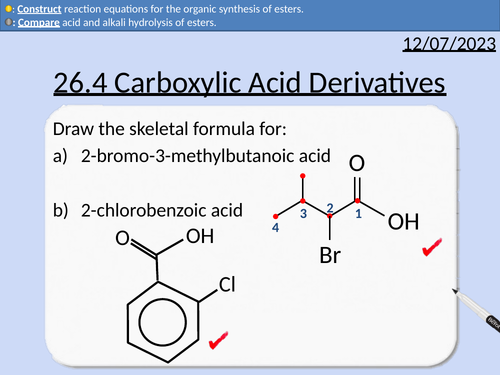
A level Chemistry: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
OCR A level Chemistry: 26.3 Carboxylic Acids
This PowerPoint is a whole lesson included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Naming acyl chlorides
Naming acid anhydrides
Naming esters
Esterification
Acid hydrolysis of esters
Alkali hydrolysis of esters
Producing acyl chlorides from carboxylic acids
Producing carboxylic acids from acyl chlorides
Producing esters from acyl chlorides and phenols
Primary, secondary, and tertiary molecules
Producing primary amides from acyl chlorides
Producing secondary amides with acyl chlorides
Producing esters and carboxylic acids wirh acid anhydride
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Nuclear Physics
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 26 Nuclear Physics is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
26.1 Einstein’s Mass-Energy Equation
26.2 Binding Energy
26.3 Nuclear Fission
26.4 Nuclear Fusion
Mass-energy is a conserved quantity
Einstein’s mass-energy equation
Particle and antiparticle annihilate each other
Rest mass and increasing mass with increased kinetic energy
Interpretation of mass-energy equivalence
Definition of mass defect
Definition of binding energy
Binding energy per nucleon
Calculating mass defect, binding energy, and binding energy per nucleon.
Explaining nuclear stability
Fuels in nuclear fission reactors
Moderators and thermal neutrons
Conservation of mass-energy
Energy released in fission reactions
Control rods
Nuclear waste management
Conditions for nuclear fusion
Binding energy and released energy
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Quantum Physics
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 4: Quantum Physics.
All presentations are full lesson PowerPoints with worked examples and homeworks with complete worked answers.
The Photon Model
Energy of a single photon
Converting from electron-volts to Joules.
Frequency of the electromagnetic spectrum
Determining Plank’s constant with LEDs
Threshold potential difference difference
Photoelectric Effect
Threshold frequency
Producing photoelectrons
Kinetic energy of photoelectrons
Linking frequency and wavelength
The electromagnetic spectrum, frequency and energy.
Einstein’s Photoelectric Equation
The photoelectric equation
Work function and Kinetic Energy
Determining work function from a graph
Determining threshold frequency from a from graphical analysis.
Determining Plank’s constant from graphical analysis.
Wave Particle Duality
deBroglie wavelength equation
Diffraction of electrons and protons
Comparing wavelengths of particles with different masses
Kinetic energy and wavelength

GCSE Physics: EM waves - Uses and Dangers
This presentation cover the OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P5.2.2 Uses and Dangers of EM radiation. PowerPoint includes student activities with full worked answers.
Recall that light is an electromagnetic wave
Give examples of some practical uses of electromagnetic waves in the radio, micro-wave, infra-red, visible, ultraviolet, X-ray and gamma-ray regions
Describe how ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays can have hazardous effects, notably on human bodily tissues.
Explain that electromagnetic waves transfer energy from source to absorber to include examples from a range of electromagnetic waves
Precautions for ultra-violet waves, X-rays and gamma rays

GCSE Physics: Magnets and Magnetic Fields
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.1.1 Magnets and Magnetic Fields.
Rules for repulsion and attraction
Magnetic Field Line Rules
Magnetic field density and magnetic force
Modeling the Earth as a Bar Magnet
Permanent and Induced Magnets
Magnetic Domains
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Thermal Physics
OCR A level Physics: Thermal Physics apart of the Module 5: Newtonian World and Astrophysics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.

OCR AS Chemistry: 17.2 Infrared Spectroscopy
OCR AS Chemistry: 17.2 Infrared Spectroscopy
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities, animated answers, homework questions with answers provided.
This lesson covers:
Absorb infrared radiation increasing vibrations
What determines the magnitude of vibration
Fingerprint region
Identifying peaks
Bundle

OCR A level Physics: Particle Physics
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 24 Particle Physics is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
24.1 Alpha-particle scattering experiment
24.2 The Nucleus
24.3 Antiparticles, Leptons, & Hadrons
24.4 Quarks
24.5 Beta decay
Developments of scientific models
Thompson’s plum-pudding model
Rutherford’s nuclear (planetary) model
Rutherford’s experiment, observations, and conclusions
Using Coulomb’s law to find the minimum distance between particles
Nucleons
Isotopes
Nuclear notation
Atomic mass units (u)
Radius for atomic nucleus equation
Volume and density of atomic nuclei
The strong nuclear force
Antiparticles, their properties, and symbols
Particle and antiparticle annihilation
The four fundamental forces (strong nuclear, weak nuclear, electromagnetic, and gravitational forces) and their properties.
Definition and examples of hadrons and leptons.
The Standard Model of particle physics
Quarks, anti-quarks and their charges
Baryons and mesons
Properties of neutrinos
Nuclear notation
Nuclear decay equations
Beta-plus and beta-minus decays
Quark transformation

GCSE Biology: Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Biology 9-1 B1.4.3 Factors Affecting Photosynthesis
This PowerPoint is a whole lessons included with student activities and animated answers.
Definition for rate of photosynthesis
The rate of photosynthesis affects the rate of biomass
Limiting factors include, light level, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Graphs for rate of photosynthesis against light level, carbon dioxide concentration, and temperature.
Plotting data graphs.
Exam questions.

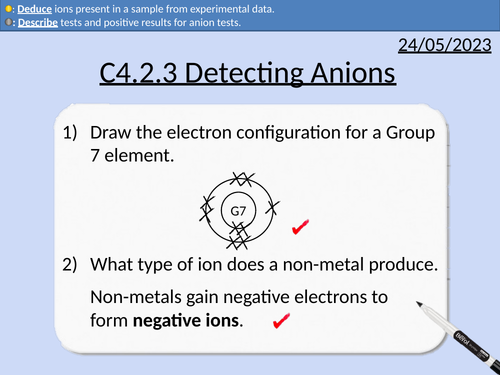
GCSE Chemistry: Detecting Anions
This PowerPoint presentation with worked examples and student questions covers:
Definitions for anions, cations, anodes, cathodes.
Tests for carbonate ions
Tests for sulfate ions
Tests for halide ions
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Spectroscopy
OCR A level Chemistry: Chromatography and Spectroscopy is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
29.1 Chromatography and Functional Group Analysis
29.2 Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Spectroscopy
29.3 Carbon-13 NMR Spectroscopyy
29.4 Proton NMR Spectroscopy
29.5 Interpreting Proton NMR Spectra
29.6 Combined Techniques
Thin layer chromatography (TLC)
Rf values
Gas chromatography (GC)
Gas chromatograms
Retention time and peak integrations
Calibration curves from retention time and relative peak area
Differentiation of functional groups: alkene, primary and secondary alcohols, aldehydes, cabonyl compounds, carboxylic acids, and haloalkes.
Nuclear Spin
Resonance
Tetramethylsilane (TMS)
Chemical Shift áşź
Identifying different carbon environments
The types of carbon environment
The amount of chemical shift áşź / ppm
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
The spin-spin splitting pattern (n + 1)
Predicting proton NMR spectra for molecules
Identifying the number of different proton environments
Identifying the types of proton environment and chemical shifts
Integration traces (area of peaks) and relative number of protons
Percentage yield to determine empirical formula
Mass spectra
Infrared spectra
Carbon-13 NMR spectra
Proton NMR spectra

GCSE Physics: Forces and Fleming's Left Hand Rule
This presentation covers OCR Gateway Physics 9-1 P4.2.1 Forces, Current and Fleming’s Left Hand Rule.
This presentation includes:
Interacting Magnetic Field Lines
Increasing Magnitude of the force on a current carrying conductor
Applying Fleming’s Left Hand Rule
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Foundations of Physics
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 2: Foundations of Physics.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from SI units to vector analyis with sine and cosine rules.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Electrical Circuits
OCR AS level Physics presentations for module 4: Energy, Power, and Resistance.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
This covers topics from Kirchhoff’s laws to potential dividers and sensing circuits.
Bundle

OCR AS level Physics: Motion
OCR AS level Physics: Forces and Motion is a part of the Module 3: Forces and Motion.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
These are fully updated PowerPoints will all exercises with full worked solutions.
Bundle

OCR A level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis
OCR A level Chemistry: Organic Synthesis is apart of the Module 6: Organic Chemistry and Analysis.
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
28.1 Carbon-Carbon Bond Formation
28.2 Further Practical Techniques
28.3 Further Synthetic Routes
Forming nitriles from haloalkanes
Forming nitriles from aldehydes and ketones
Forming amines from nitriles (reduction)
Forming carboxylic acids from nitriles (hydrolysis)
Friedel-Crafts alkylation of benzene
Acylation of benzene with acyl chloride
Filtration under reduced pressure
Purification through Recrystallisation
Preparation of Melting Point Sample
Melting point determination with an electric heater
Melting point determination with a Thiele tube
Functional groups
Reactions of benzenes
Reactions of phenols
Common reactions between different functional groups
Reaction conditions and reagents