Last updated
17 July 2025
Share this
OCR A level Physics: Chapter 27 Medical Imaging is apart of the Module 6: Particle and Medical Physics
All presentations come with worked examples, solutions and homeworks.
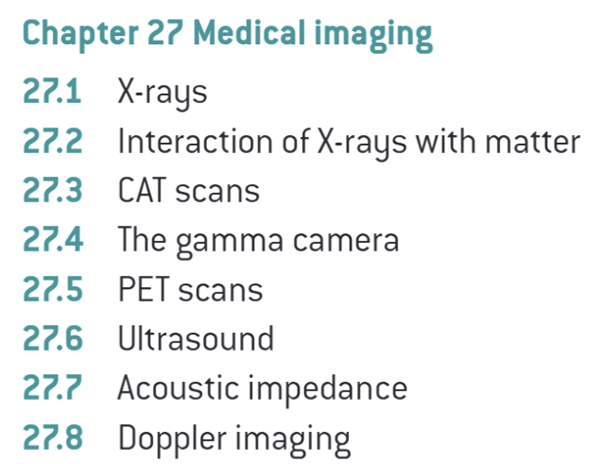
27.1 X-rays
27.2 Interaction of X-rays with matter
27.3 CAT Scans
27.4 The Gamma Camera
27.5 PET Scans
27.6 Ultrasound
27.7 Acoustic Impedance
27.8 Doppler Imaging
- The basic structure of an X-ray tube
- How accelerating potential difference affect electrons and X-rays produced.
- Production of X-ray photons
- Maximum wavelength, frequency and energy of X-rays
- Simple scattering
- Photoelectric effect
- Compton scattering
- Pair production
- Attenuation coefficients and calculations
- Contrast medium
- Therapeutic use of X-rays
- CAT stands for computerised axial tomography.
- State the advantages and disadvantages of CAT scans over traditional X-rays.
- Describe how a CAT scanner works.
- Radiopharmaceuticals
- Tracers - Penetration power and half-life
- Technetium-99m Decay Route
- The structure and functions of a gamma camera - Collimator, Scintillator, Photomultiplier tubes.
- PET stands for positron emission tomography.
- Radiopharmaceutical - Fluorine-18 and Carbon-11
- Nuclear equations
- The production of Fluorine-18
- How PET scanners operate
- Advantages and disadvantages of PET
- Frequency range of ultrasound
- The operation of transducers
- The piezoelectric effect
- A-scans and B-scans
- Acoustic impedance
- Intensity Reflection Coefficient
- Acoustic Matching
- The Doppler Effect
- Doppler Scans
- The angle between the transducer and the blood vessel
- Calculating the speed of blood from a Doppler scan
Reviews
Select overall rating(no rating)
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.