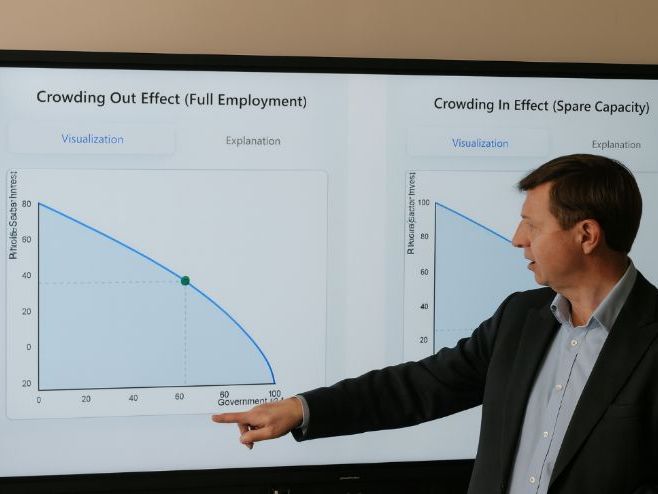

This interactive resource, the Crowding In/Out Effect Visualiser, is designed as both a teaching and learning tool to help students explore the complex relationship between government deficit spending and private sector investment. It provides a dynamic way of visualising the economic concepts of crowding out, which occurs when the economy is operating at full employment, and crowding in, which emerges when spare capacity exists. Rather than relying solely on static diagrams in textbooks, this resource allows learners to manipulate variables directly and see in real time how economic choices and trade-offs play out along the production possibility frontier (PPF).
The visualiser is split into two main sections: one dedicated to crowding out and the other to crowding in. In the crowding out section, learners adjust sliders to represent government spending and private investment when resources are fully employed. They can immediately see how increased government borrowing shifts the position along the PPF, highlighting the direct trade-off between public and private spending. This builds understanding of opportunity cost, resource allocation, and the constraints of full employment. The crowding in section instead focuses on economies operating below capacity. Here, learners begin with lower levels of spending and can activate the “accelerator effect.” This step-by-step simulation illustrates how government stimulus can spark private sector optimism, increase investment, and push the economy closer to full capacity. By experiencing the accelerator principle in action, students can develop a clearer sense of how fiscal policy can drive multiplier effects in practice.
The resource is enhanced further with explanatory tabs that guide learners through the mechanisms behind each effect, alongside a dedicated theory section. Here, students are introduced to the contrasting perspectives of Keynesian, Monetarist, and Neo-Classical schools of thought. Each perspective is clearly explained, allowing learners to compare and evaluate differing economic arguments. This provides a platform for higher-level critical thinking, as students are not only observing how the mechanisms work but also engaging with the theoretical debates surrounding the effectiveness of government intervention.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.