
Excretory System: The Kidneys (A Levels & IGCSE Notes)
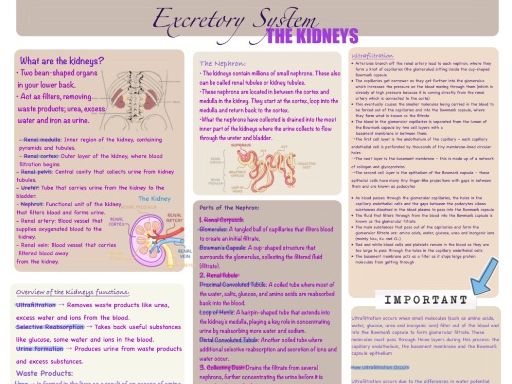
The kidneys are vital organs of the excretory system responsible for filtering blood to remove metabolic wastes and excess substances, primarily maintaining the body’s internal balance. Each kidney contains numerous nephrons—the functional units—that facilitate the processes of filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion.
Structure of the Kidney:
- Cortex: The outer region where initial filtration occurs.
- Medulla: Contains the loops of Henle that help concentrate urine.
- Renal Pelvis: Collects urine before it passes to the ureter.
- Nephrons: Microscopic structures comprising the glomerulus, Bowman’s capsule, proximal convoluted tubule, Loop of Henle, distal convoluted tubule, and collecting duct.
Functions of the Kidneys:
- Filtration of blood: Removing waste products like urea, creatinine, and excess salts.
- Reabsorption: Returning essential substances (glucose, water, salts) to the bloodstream.
- Secretion: Removing additional wastes and balancing pH.
- Excretion: Producing urine that carries wastes out of the body.
Process of Urine Formation:
- Filtration in the Glomerulus: Blood pressure forces plasma and small molecules into Bowman’s capsule.
- Reabsorption: Useful substances like glucose, amino acids, and most water are reabsorbed into the blood via the proximal tubule, Loop of Henle, and distal tubule.
- Secretion: Additional wastes are secreted into the tubule.
- Excretion: The resulting urine flows into the collecting duct, then to the renal pelvis, and finally out via the ureter.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions.
Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.